
Thyroid Disease
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. Dr. Frances Mei Hardin works closely with endocrinologists and other specialists to address surgical treatments of common thyroid issues. Some of the most common conditions addressed include goiters, thyroid nodules and cancer.
Goiter
Goiter is the irregular growth of the thyroid gland. Common causes include iodine deficiency, Hashimoto's disease, Graves' disease, thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer. A small goiter may not require treatment. However, if the goiter causes difficulty swallowing or breathing, surgery may be required to remove all or part of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid nodules
Thyroid nodules are common and more than 95 percent are noncancerous (benign). These nodules include:
- Multinodular goiter: When the pituitary gland in the brain creates too much thyroid stimulating hormone, the result is an enlargement of the thyroid gland known as goiter. Most goiters may be treated medically with thyroid hormone pills; however, surgery is necessary if the goiter is large or does not stop growing after taking thyroid hormones. If left untreated, this may result in pressure against the trachea (airway) or esophagus.
- Benign follicular adenoma: If follicular cells are contained in a thyroid nodule, the condition is considered benign. If cells have invaded surrounding tissue, the diagnosis may be cancer.
- Thyroid cysts: Cysts are nodules that are filled with fluid; however, if the nodule has both fluid and solid features, it is considered a complex nodule. If this type of nodule causes neck pain or difficulty swallowing, it should be removed.
Thyroid issues are generally diagnosed with an initial blood test. If thyroid levels are abnormal, next steps may include an ultrasound of the thyroid and needle biopsy of any nodules to determine if they are cancerous.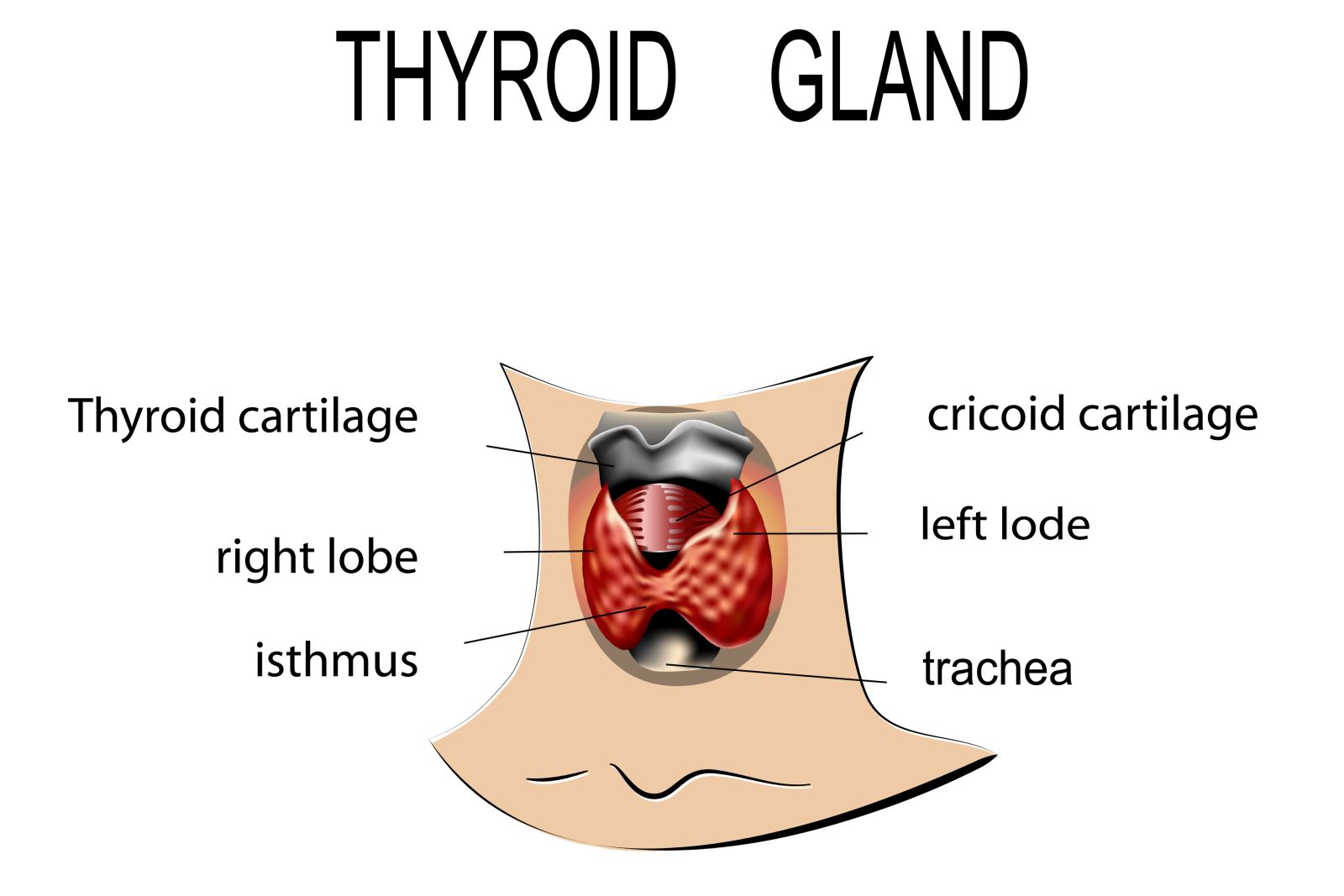
cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, the exact cause of most thyroid cancers is not yet known but family history, smoking, obesity, low iodine levels and exposure to radiation are considered risk factors. Surgery is the main treatment and may include removing one lobe of the thyroid or the entire thyroid. This is typically performed through a small incision across the front of the neck. If cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes in the neck, they will be removed during your thyroid surgery.