COLUMBIA, Tenn. — Antibiotics are important medications that can be used to treat many serious infections for children and adults. When used without need, however, antibiotics can lead to complications for an individual patient as well as the community. During Antibiotic Awareness Week November 13-19, Maury Regional Health encourages the public to learn more about proper use of antibiotics.
An antibiotic is a medication prescribed by a health care provider to treat and prevent infections caused by bacteria. Since the discovery of penicillin in the late 1920s, many different forms of antibiotics have been used to treat bacterial illnesses. Although beneficial for their intended purpose, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that the overuse of antibiotics is contributing to bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, as well as serious infections such as Clostridium difficile—known as C-diff. The World Health Organization classifies antibiotic resistance as a pressing threat to the world’s health.
According to Dr. Deborah Goldsmith, an infectious disease specialist on the medical staff at Maury Regional Medical Center, antibiotics are only effective in treating bacterial infections.
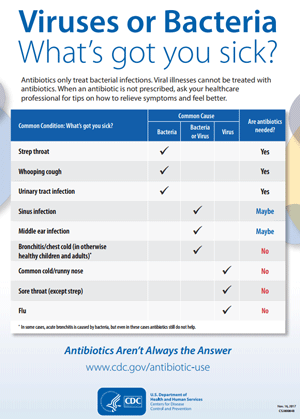
Examples of illnesses that may be caused by bacteria and, therefore, may respond to antibiotics are:
- Strep throat
- Urinary tract infection
- Whooping cough
Antibiotics do not work to treat viral illnesses. Some illnesses that are caused by viruses and, therefore, should not be treated with antibiotics are:
- Cold
- Bronchitis
- Flu
- Runny nose
- Sore throat (except those caused by strep)
Antibiotics may be helpful when treating some ear infections and sinus infections depending on the cause. In addition to treating a current bacterial infection, antibiotics may be given to prevent infection in those with weakened immune systems, such as those with cancer or patients having surgery.
According to Dr. Goldsmith, you should never take an antibiotic that has been prescribed for a previous illness or to another person. You should refrain from encouraging a provider to prescribe an antibiotic shot or pill if your illness is caused by a virus as overuse of antibiotics may reduce their effectiveness when they are needed to treat a bacterial infection.
"Taking an antibiotic when you do not have a bacterial infection will not help to relieve your symptoms and can actually make it harder for your body to fight future infections,” said Dr. Goldsmith.
Consult with your health care provider when you are sick to determine if the illness is caused by a virus or bacteria. If an antibiotic is not the right treatment, ask about ways to relieve symptoms using other types of medications or remedies.
To learn more about antibiotic use, visit CDC.gov or visit MauryRegional.com/AntibioticAware.
Additional resources and information
Visit CDC.gov

